Optimizing the Plugin Prompt—the generated interface that explains your plugin to ChatGPT—can significantly enhance your ChatGPT plugin's performance. In this blog post, we'll dive into how ChatGPT Plugins compile your OpenAPI specification and ai-plugin.json files into a Plugin Prompt. We'll also explore strategies for optimizing the available space in the prompt, resulting in more accurate and contextually relevant plugin interactions.
The Significance of the Plugin Prompt
The Plugin Prompt is a dynamically generated Typescript pseudo-code that serves as a vital link between ChatGPT and your plugin. Its construction relies primarily on the description_for_model property in the ai-plugin.json file and the information contained in your OpenAPI specification.
The Plugin Prompt plays an essential role in determining how ChatGPT interprets and interacts with your plugin. By fine-tuning the Plugin Prompt, you can significantly improve the accuracy and context-awareness of your plugin's responses, leading to an enhanced user experience.
Capitalizing on the Prompt Space
While the DESCRIPTION_FOR_MODEL property offers the most space with 8,000 characters, it's crucial not to underestimate the importance of other properties from the OpenAPI spec in the Plugin Prompt.
Each API endpoint defined in the OpenAPI spec includes two description properties that are also incorporated into the Plugin Prompt. Since each description can be up to 200–300 characters (200 according to the docs, 300 in my tests), that means an API with ten endpoints could gain an additional 4,000–6,000 characters of prompt space with efficient use of the properties in the OpenAPI spec.
Notable OpenAPI Properties in the Plugin Prompt
Path/Type Descriptions
The OpenAPI Path Description, if available, appears immediately before the type declaration in the dynamically generated pseudo-code namespace of the Plugin Prompt. If the Path Description is unavailable, the OpenAPI Summary is used instead. This ensures that the prompt has relevant information about the specific API endpoint.
Component/Property Descriptions
Each pseudo-code type contains properties generated from OpenAPI component property descriptions. It's important to note that only descriptions specific to request properties are included. This approach is advantageous because it provides more prompt space per component, as each description can be another 300-character prompt. Schema-level descriptions and properties of response objects are not included in the Plugin Prompt.
Decoding the Plugin Prompt
To gain a better understanding of the Plugin Prompt output, let's examine an example using a simple OpenAPI spec and an ai-plugin.json file. The main experiment below tests all common properties in the OpenAPI spec to determine which properties are included in the Plugin Prompt.
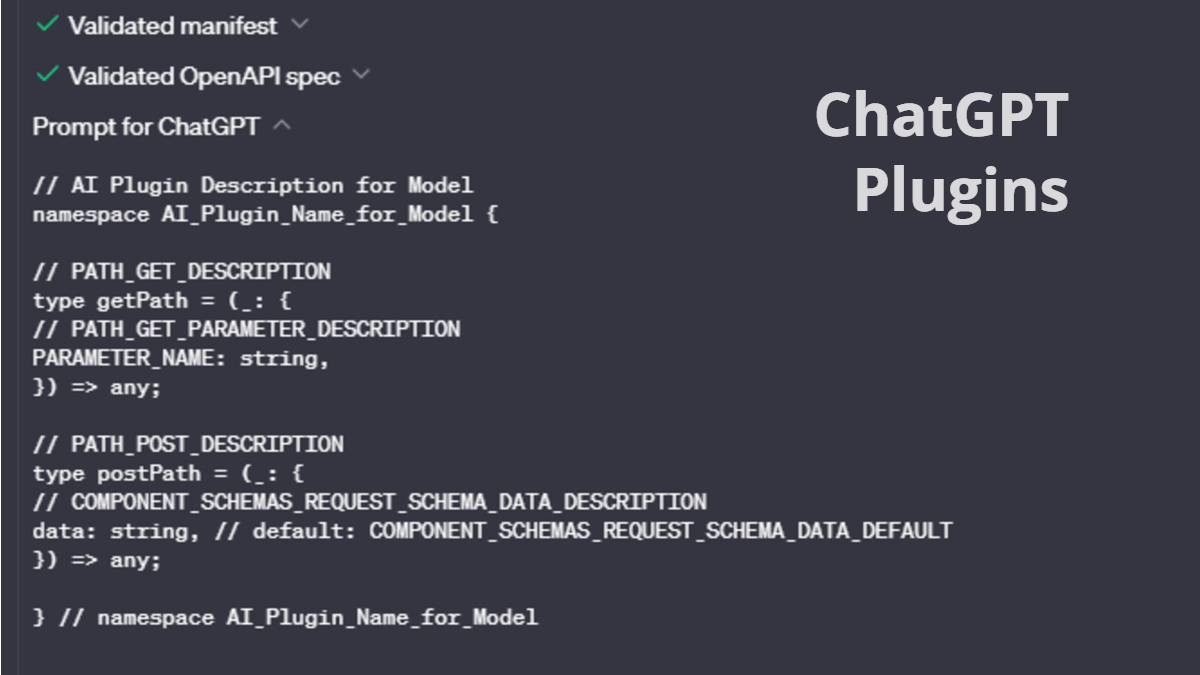
Example Plugin Prompt
// DESCRIPTION_FOR_MODEL
namespace NAME_FOR_MODEL {
// PATH_GET_DESCRIPTION
type getPath = (_: {
// PATH_GET_PARAMETER_DESCRIPTION
PARAMETER_NAME: string,
}) => any;
// PATH_POST_DESCRIPTION
type postPath = (_: {
// COMPONENT_SCHEMAS_REQUEST_SCHEMA_DATA_DESCRIPTION
data: string, // default: COMPONENT_SCHEMAS_REQUEST_SCHEMA_DATA_DEFAULT
}) => any;
} // namespace NAME_FOR_MODEL
Let's look at an OpenAPI specification and ai-plugin.json file to see how these files are converted into the Plugin Prompt above. Property values are in ALL CAPS for easy mapping between the source files and the Plugin Prompt.
ai-plugin.json
{
"schema_version": "v1",
"name_for_model": "NAME_FOR_MODEL",
"description_for_model": "DESCRIPTION_FOR_MODEL",
…
}
OpenAPI spec
openapi: 3.0.0
info:
title: EXAMPLE_API_TITLE
description: EXAMPLE_API_DESCRIPTION
version: 1.0.0
servers:
- url: http://localhost:5003
variables:
apiDomain:
default: example.com
description: EXAMPLE_SERVER_VARIABLE_API_DOMAIN_DESCRIPTION
paths:
/path:
get:
tags:
- PATH_GET_TAG
summary: PATH_GET_SUMMARY
description: PATH_GET_DESCRIPTION
operationId: getPath
parameters:
- name: PARAMETER_NAME
in: query
description: PATH_GET_PARAMETER_DESCRIPTION
required: true
schema:
type: string
responses:
200:
description: PATH_GET_RESPONSE_200_DESCRIPTION
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: "#/components/schemas/ResponseSchema"
400:
description: PATH_GET_RESPONSE_400_DESCRIPTION
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: "#/components/schemas/ErrorSchema"
default:
description: PATH_GET_RESPONSE_DEFAULT_DESCRIPTION
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: "#/components/schemas/ErrorSchema"
post:
tags:
- PATH_POST_TAG
summary: PATH_POST_SUMMARY
description: PATH_POST_DESCRIPTION
operationId: postPath
requestBody:
description: PATH_POST_REQUEST_BODY_DESCRIPTION
required: true
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: "#/components/schemas/RequestSchema"
responses:
200:
description: PATH_POST_RESPONSE_200_DESCRIPTION
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: "#/components/schemas/ResponseSchema"
400:
description: PATH_POST_RESPONSE_400_DESCRIPTION
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: "#/components/schemas/ErrorSchema"
default:
description: PATH_POST_RESPONSE_DEFAULT_DESCRIPTION
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: "#/components/schemas/ErrorSchema"
components:
schemas:
RequestSchema:
type: object
properties:
data:
type: string
description: COMPONENT_SCHEMAS_REQUEST_SCHEMA_DATA_DESCRIPTION
default: COMPONENT_SCHEMAS_REQUEST_SCHEMA_DATA_DEFAULT
description: COMPONENT_SCHEMAS_REQUEST_SCHEMA_DESCRIPTION
required:
- data
ResponseSchema:
type: object
properties:
data:
type: array
items:
$ref: "#/components/schemas/DataSchema"
description: COMPONENT_SCHEMAS_RESPONSE_SCHEMA_DESCRIPTION
DataSchema:
type: object
properties:
id:
type: string
description: COMPONENT_SCHEMAS_DATA_SCHEMA_ID_DESCRIPTION
name:
type: string
description: COMPONENT_SCHEMAS_DATA_SCHEMA_NAME_DESCRIPTION
default: COMPONENT_SCHEMAS_DATA_SCHEMA_NAME_DEFAULT
description: COMPONENT_SCHEMAS_DATA_SCHEMA_DESCRIPTION
required:
- id
- name
ErrorSchema:
type: object
properties:
message:
type: string
description: COMPONENT_SCHEMAS_ERROR_SCHEMA_MESSAGE_DESCRIPTION
code:
type: integer
format: int32
description: COMPONENT_SCHEMAS_ERROR_SCHEMA_CODE_DESCRIPTION
description: COMPONENT_SCHEMAS_ERROR_SCHEMA_DESCRIPTION
required:
- message
- code
Description vs. Summary Experiment
In cases where the Path Description is not provided, the OpenAPI Summary is used instead. The following example demonstrates this scenario:
Plugin Prompt
// DESCRIPTION_FOR_MODEL
namespace NAME_FOR_MODEL {
// PATH_GET_SUMMARY <---- [**THE CHANGE: REPLACED DESCRIPTION WITH SUMMARY**]
type getPath = (_: {
// PATH_GET_PARAMETER_DESCRIPTION
PARAMETER_NAME: string,
}) => any;
// PATH_POST_DESCRIPTION
type postPath = (_: {
// COMPONENT_SCHEMAS_REQUEST_SCHEMA_DATA_DESCRIPTION
data: string, // default: COMPONENT_SCHEMAS_REQUEST_SCHEMA_DATA_DEFAULT
}) => any;
} // namespace NAME_FOR_MODEL
OpenAPI spec
openapi: 3.0.0
info:
title: EXAMPLE_API_TITLE
description: EXAMPLE_API_DESCRIPTION
version: 1.0.0
servers:
- url: http://localhost:5003
variables:
apiDomain:
default: example.com
description: EXAMPLE_SERVER_VARIABLE_API_DOMAIN_DESCRIPTION
paths:
/path:
get:
tags:
- PATH_GET_TAG
summary: PATH_GET_SUMMARY
# description: PATH_GET_DESCRIPTION <---- [**THE CHANGE: REMOVED DESCRIPTION**]
operationId: getPath
parameters:
- name: PARAMETER_NAME
in: query
description: PATH_GET_PARAMETER_DESCRIPTION
Wrapping Up
Optimizing the Plugin Prompt is crucial for enhancing the performance and user experience of your ChatGPT plugin. You can create more precise and contextually relevant plugin interactions by understanding what is included in the Plugin Prompt and how to use the available space effectively. As you develop your ChatGPT plugin, remember that the OpenAPI spec should be considered prompt engineering space to build the best possible user experience for your ChatGPT plugin.